Virtualization on Fedora
R
Getting started with virtualization on Fedora
Fedora uses the
libvirt
family of tools as its virtualization solution, as an alternative to Virtualbox or VMWare.
Detailed instructions can also be found here Docs
run the following command to install the mandatory, default and optional packages;
$ sudo dnf group install --with-optional virtualization
after the packages install, start the libvirtd service:
$ sudo systemctl start libvirtd
To start the service on boot, run;
$ sudo systemctl enable libvirtd
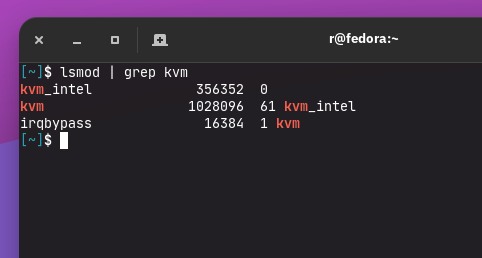
Verify that the KVM kernel modules are properly loaded:
$ lsmod | grep kvm
Manage virtual machines with virt-manager
You can download it from the store if it's not already installed.
From there you can install and run virtual machines!
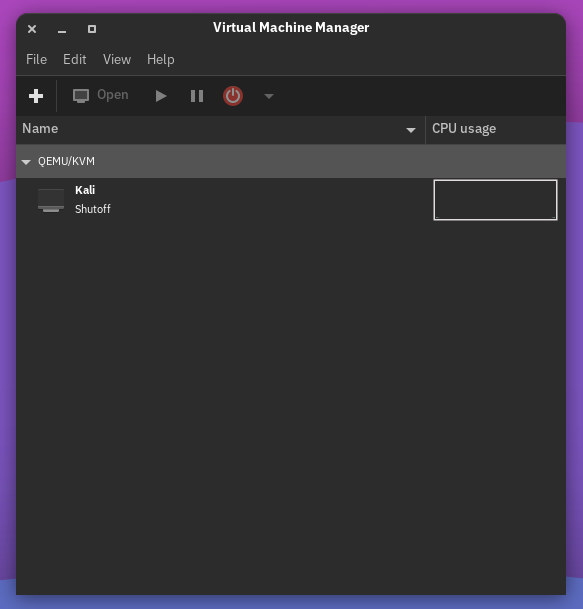
We now have another option to run virtual machines for our lab.
In our next post we will go through the steps to set up a Kali linux virtual machine.